4대 조직: 결합, 상피, 근육, 신경
신경조직 = neuron + neuroglia
Neuron
- 신경계에서 자극을 받아들이고 정보를 처리하여 효과기에 전달하여 반응을 일으킴
- 자극의 수용(excitability, 흥분성)
- 신경흥분의 전달(conductivity, 전도성)
- 신경세포 = 심장 외에 스스로 흥분을 일으키는 유일한 세포
- 뇌/척수/ganglion에 존재
- 모양 / 크기 다양
- 성인 정상 신경세포 → 세포분열/증식 X
종류
| ① 역할 | sensory |
| interneuron | |
| motor | |
| ② neurite 수, 길이, 분지양상 | unipolar |
| bipolar | |
| multipolar | |
| ③ 크기 | Golgi Type I |
| Golgi Type II |
| ② neurite 수, 길이, 분지양상 | ||
| 형태 분류 | 신경돌기의 배열 | 위치 |
| unipolar | 세포체로부터 돌기가 하나 나와서 짧은 거리 동안 진행한 후에 갈라진다. | DRG |
| bipolar | 세포체의 양끝에서 돌기가 하나씩 나옴 | retina bipolar cell, vestibular / cochlear ganglion, sensory neuron |
| multipolar | 다수의 가지돌기, 하나의 긴 축삭 | 뇌와 척수의 신경로, 말초신경, 척수의 운동신경세포 |

| ③ 크기 | ||
| 형태 분류 | 신경돌기의 배열 | 위치 |
| Golgi Type I | 긴 하나의 축삭 | 뇌와 척수의 tract, 말초신경, 척수의 운동신경세포 대뇌겉질(purkinje cell) 소뇌겉질(pyramidal cell) |
| Golgi Type II | 축삭이 짧음 가지돌기들 때문에 별 모양 | 대뇌겉질 소뇌겉질(stellate, granule cell) |


Cell body
1. nucleus
- 둥글고 크며 세포체의 중간에 위치
- 복제 X. only 발현.
1) chromatin type
(1) euchromatin: active mRNA transcription
(2) barr body: 여자 inactive X chromosome
2. nucleolus
- active rRNA transcription
- cajal body = coiled body; snRNP; 단백질 + RNA
Nissl body
- abundant, 평행하게 배열된 rER cisterna
- active site of protein synthesis
- basophilic: toluidine blue
- chromatolysis: nissl body가 손상돼 제대로 안 보이는 현상
- axon hillock ~ axon에 없음; 단백질 합성 X

Cresyl Violet 염색 : Nissl Body(rER)
Cajal’s Silver Nitrate 염색: Cajal(Coiled) Body
Cytoskeleton
- microtubule(MAP)
- actin filament: microfilament
- intermediate filament: neurofilament
| I, II | Keratin |
| III | Vimentin, desmin, GFAP |
| IV | Nestin |
| V | nuclear lamin |
주요 Neurofilament들
① Tau: microtubule을 안정화시키는 단백질. 치매 환자들에서 많이 축적 → 인지장애
② Neurofibrils(NF): 정상.
③ Neurofibrillary tangles: hyperphosphorylated tau 단백질이 과도히 뭉쳐있는 것. AD의 중요 표지 marker
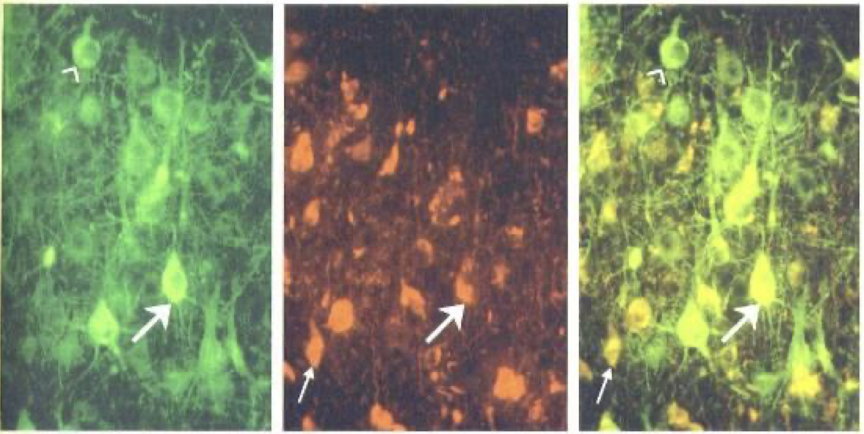
Pigment
① Lipofuscin: 노화와 관련; lysosome 작용으로 인한 무해한 대사부산물
② Melanin: substantia nigra(dopaminergic neuron); catecholamine 합성과 관련.
Dementia (치매)
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy |
| Dementia pugilistica Punch-drunk syndrome Boxer’s Syndrome Post-Concussion Syndrome |
|
| 지속적인 뇌손상 → tau 단백질 축적 → dementia (cognitive impairment) & depression |
|
| NFTs + pre-tangles | NFTs + pre-tangles |
| prominent astrocytic tangles | |
| CTE stages I-II: NFTs in cerebral cortex, usually frontal lobe 생각 관련 부위 |
Braak stages I-III NFTs in entorhinal cortex, amygdala, hippocampus 기억 관련 부위 |
| CTE stages III-IV: High density of NFTs in widespread cortical areas + medial temporal lobe |
Braak stages Iv-VI High density of NFTs in widespread cortical areas + medial temporal lobe |
| patchy, irregular distribution | uniform distribution |
Neuron의 손상
| 1. 급성신경세포 손상(acute neuronal injury) | |
| 원인 | ① cytotoxic stress ② hypoxia / ischemia ③ infection ④ toxin |
| 형체학적 특징 | ① cell body shrinkage / angularity ② nucleus pyknosis(응축) ③ nucleolus disappearance ④ intense eosinophilia of the cytoplasm - red neuron : “red dead” neuron ⑤ loss of Nissl substance : H&E 염색으로 손상 12-24시간 후로 검출 가능 |
| 위치 | ① cortex(layers 3, 5) ② hippocampus(CA1) ③ cerebellar Purkinje layer |
| 2. 아급성 및 만성 신경세포손상(subacute & chronic neuronal injury = degeneration; 변성) | |
| 증상 | trans-synaptic degeneration 신경세포 손상이 천천히 일어남 |
| 3. 축삭반응(axonal reaction) | |
| 4. Neuronal inclusions & Intracytoplasmic deposits | |
| 원인 | Viral Infections 신경세포는 분열하지 않기에 정상 상태에서는 무균상태이다 |
| 증상 | AD: Neurofibrillary tangles PD: Lewy bodies |


Pyknosis(karyopyknosis) : irreversible condensation of chromatin in the nucleus of a cell undergoing necrosis / apoptosis
Chromatolysis: 피로/신경손상(axon 손상) 시 세포체 부음
→ nissl body가 세포 가장자리로 이동 / 사라짐 → 안 보임
+ 핵이 가장자리로 이동
Neurites(Cell Processes)
1. Dendrite
1) dendritic spine(가시돌기가시)
- mental retardation : 가시돌기가시 발달 이상; 같은 자극 줘도 기억 X
⇒ dendritic spine은 기억/지능에 중요하다
- structural basis of memory
- Fragile X Syndrome
2. Axon
1) Axon Hillock: Nissl Body X
2) 분지양상:
(1) Axon Collateral
(2) Telodendron
3) Initial Segment: action potential(AP)
- Na+ channel이 고밀도로 분포
4) Boutons Terminal
5) Axolemma
6) Axoplasma: Nissl Body, Golgi X
Immunohistochemical Markers
- Neurofilament Protein(NF)
- Neuron Specific Enolase(NSE)
- Synaptophysin
- NeuN
신경아교세포(neuroglia)
1. CNS에 있는 glia
1) astrocyte
(1) protoplasmic: 회색질; branched process
(2) fibrous: 백색질; long, thin process
2) microglia
3) oligodendrocyte
(1) perineuronal satellite cell
(2) interfascicular cell
4) ependymal cell
2. PNS에 있는 glia
1) satellite(capsule) cell : ganglion
2) schwann cell : peripheral n. & ganglion
CNS Neuroglia

| 1. Astrocyte | |
| 기능 | 1. Developmental 1) astroglia are stem elements of the CNS: regulation of neuro- & gliogenesis 2) Neuronal pathfinding 3) Regulation of synaptogenesis |
| 2. Structural 1) nervous system의 scaffold 형성 2) defines the functional architecture of the brain & spinal cord 3) form a continuous syncytium & integrate other neural cells |
|
| 3. Vascular : formation & regulation of the BBB 1) Formation of the glial-vascular interface 2) Regulation of Cerebral Microcirculation |
|
| 4. Metabolic 1) Provide energy substrates for neurons 2) Collecting neuronal waste |
|
| 5. Control of CNS microenvironment 1) Na+ / K+ ATPase + Kir4.1 → K+ 재분배, extracellular pH 조절 |
|
| BBB | BBB 구성 세포 = endothelial cell + pericyte + astrocyte BBB 단백질 : K+ channel, Glucose transporter, gap junction astrocyte: gap junction 형성 Aqp4: capillary로 물 수송 조절하는 단백질 뇌질환에서 edema 일어나면 큰일남! |
| 인간 | 고등생물일수록 synapse 작용 많음; astrocyte 크고 복잡 |
| 물리적 장벽 | tripartite synapse = astrocyte + pre + post prevent spill-over & diffusion of released molecules to ECS |
| 다양성 | (1) Protoplasmic: 대부분 회색질에; branched process (2) Fibrous: mostly in white matter, long-thin process (3) Radial astrocyte (glia) 발생중 (4) Perivascular or Marginal astrocyte: pia mater (5) Velate astrocyte: cerebellum (6) Muller cells: retina (7) Bergmann glia: cerebellum (8) Ependymal cells |
| 손상 | ① gliosis = astrogliosis = astrocyte activation = reactive astrocyte = glial cell ensheathment : 신경 손상 몇 시간 후 astrocyte가 대신 증식, 예전에 neuron들이 차지했던 공간 채움 → synaptic terminal retraction
|
② Rosenthal Fibers: astrocytic process에서 eosinophilic, thick, elongated한 구조
|
|
 |
|
| Domain | Domain Organization 각 astrocyte → 하나의 synapse 조절 → astrocyte domain으로 각각의 영역 존재 nonreactive astrocytes ↓ 손상 reactive (더 두꺼워지고 가지 많아짐; 여전히 가지 존재) epileptic brain에서 domain 사라짐 |
| Radial Glial Cell | specialized astrocyte; CNS 발달에서 중요 provide pathways for neuronal growth + targeting adult: ① Muller Cell(retina) ② Bergmann glia(소뇌) |
| 2. Microglia | |
| 특징 | 전체 glial cells의 10-20% (100-200 billion cells) = resident immune cells of the CNS |
| 위치 | entire CNS including the spinal cord white matter < gray matter |
| 기능 |  |
| 종류 | ① Surveillant: small body & long thin process ② Primed: larger body, thicker process, secondary branching ③ Transitional : highly reduced branching, thickened process, elongated body ④ Amoeboid: enlarged body with little to no branching |
 |
|
| 기원 | BM: yolk sac hemogenic endothelium → erythro-myeloid progenitors(EMPs) → yolk sac macrophages(w/o monocytic intermediates) / fetal monocytemyeloid progenitors(tissue-specific macrophages) → microglia + macrophages |
| 발달 | postnatal stage: derive from circulating monocytes |
| 성인 | 정상 뇌: resident progenitors → in situ proliferation → self renew 질병 뇌: derive from circulating progenitors(monocytes) |
| 역할 | 2가지; 서로 반대 : pro & anti inflammatory [polarization] ① perivascular resting microglia ↓ soluble mediators - cell contact ② parenchymal resting microglia ↓ proliferation / activation / quantum jumps ③ effector microglia  |
| 억제 | 건강한 경우 neuron → “do not eat me” signal → microglia attack 억제 |
| 참고 | synaptic pruning: survey environment w/ extremely motile processes + ramifications |
| 3. Oligodendrocyte | |
| 특징 | small lymphocyte-cized nucleus w/ clear halo |
| 기능 | CNS myelin 생성 / 유지 |
| 종류 | ① perineuronal satellite cell ② interfascicular cell : myelin-forming cell in CNS - premyelinating : 말이집 안 만드는 경우 - myelinating: 말이집 만드는 경우 |
| 질병 | MS: inflammatory demyelination disease
|
| 4. Ependymal Cells | |
| Ependymocyte |
|
| Tanycyte |
|
| Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cells |
|
PNS Neuroglia
| 1. Capsular(Satellite) Cell | |
| 기능 | 신경세포 주위 화학물질 조성에 영향 |
| 2. Schwann Cell | |
| 위치 | peripheral n. & ganglion |
| 분화 |  |
| 구조 | mesaxon(축삭간막) major dense line: 형질막 두 속단백질층 minor dense line: 형질막 바깥면   |
| 질병 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth(CMT) type 1 neuropathy Schwann cell에 특이적인 유전자 없음 |
| Guillain Barre Syndrome: Acute autoimmune neuritis | |
| Diabetic Neuropathy → Foot Ulcer | |

| Myelination: CNS vs PNS | ||
| Oligodendrocyte | Schwann Cell | |
| 담당 nerve fiber per 세포 |
<60 | 1 |
| 말이집마디 | O | O |
| 말이집틈새 | O | O |
| 축삭간막 | X | O |
CNS Remyelination

① normal white matter
② demyelination + OPC activation
③ OPC recruitment(proliferation + migration)
④ OPC differentiation(axon engagement & myelin sheath formation)
* CNS axon은 재생 X / myelin은 재생 O
Peripheral n. regeneration

① 말초신경 axon cut
② distal portion degenerates
③ macrophages: 남아있는 axon을 phagocytose
④ growth-related genes 발현
⑤ debris mostly cleared
⑥ proximal axon stump transforms into a growth cone + axon-growth promoting signals, neurotrophins, ECM
⑦ proliferating Schwann cells promote axon regeneration
⑧ axon has regrown
CNS Injury


① CNS axon cut
② prolonged clearing of myelin debris
③ inhibitory signals(MAG, Nogo-A) disrupt axon extension
* CNS는 basement membrane이 없기 때문에 주변에서 signal 주어 못 자라게 함
Growth-promoting properties of peripheral nerve sheaths and Schwann cells facilitate growth of damaged axons in the CNS
- optic n.는 CNS의 일부이므로 보통 재생 X
- peripheral(sciatic) nerve graft로 눈과 superior colliculus를 연결
- superior colliculus = normal target for retinal ganglion cells

'건강' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 신경해부 #4: 척수신경로(Spinal Tracts) (0) | 2024.03.24 |
|---|---|
| 신경해부 #3: 척수(Spinal Cord) (0) | 2024.03.24 |
| 신경 해부 #1: 신경계통의 구성 (0) | 2024.03.19 |
| 알구로닉 애시드(Alguronic Acid): 피부 과학에서 발견한 3가지 주목할 만한 효능 (0) | 2024.03.17 |
| 혈당 다이어트: 유주얌의 혈당실험소, CGM을 받을 수 있는 경로/절차/사용 방법 (0) | 2024.03.16 |



